A benign tumor is a noncancerous growth in the body. But like cancerous growths, they don’t spread or metastasize to other parts of the body. Benign breast tumor disease accounts for 80% of 1.6 million breast biopsies performed every year in the United States.
The terms tumor and cancer are sometimes used interchangeably which can be misleading. A tumor is not necessarily cancer. Though the exact cause of tumor pathogenesis is often unknown, it develops when cells in the body divide and grow at an excessive rate than normal. When old or damaged cells perish, they are automatically replaced with new, healthy cells and the body is able to balance cell growth and division. Cancer cells grow similarly but unlike benign tumor cells, cancerous cells can invade nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body.
Doctors use a variety of techniques to diagnose benign breast tumors. The most important aspect of diagnosis is determining if a tumor is benign or malignant. This can be determined by performing a physical examination and collecting a detailed medical history. Many internal benign tumors are found and located by imaging tests like MRI scans, mammograms ultrasounds and biopsy. Benign tumors often show a capsule or protective sac.
Not all benign tumors need treatment. Symptomless and small tumors may require a wait-and-watch approach. The removal of the tumor depends on the location of it and maybe indicated due to cosmetic reasons. Treatment of benign tumors can lead to scars that can alter one’s perception of body image with a negative impact on self-esteem or self-confidence, especially in the case of young patients.
For women with benign breast disease, both clinicians and patients prefer definitive surgical management. Considering the fact that these tumors are benign, an important factor in treatment is cosmesis. Novel minimally invasive techniques like vacuum-assisted percutaneous biopsy for breast lesions are rapidly emerging and demonstrate good efficacy, safety and cosmesis. Vacuum-assisted Breast Biopsy (VABB) also called Scarless Breast Surgery. It is a newly developed technology that does not leave any ‘scar’ on the breast post the procedure. Also, it offers a very early diagnosis of really small abnormalities (as small as 1-2mm) which are seen on ultrasound and mammography.
Scarless surgery is increasingly used for breast tumors in recent years. It has several advantages over conventional surgery, including reduced tissue damage, a smaller wound, fewer complications, minimal postoperative scarring and requires almost no recovery time.
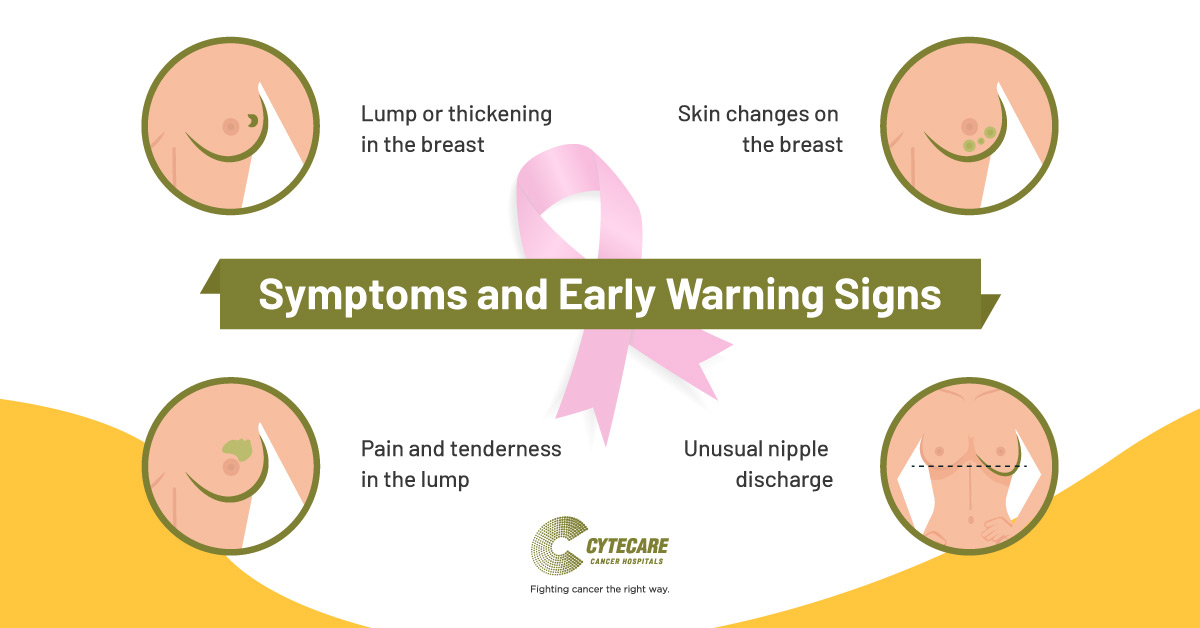
It is important to understand that though many growths and tumors turn out to be benign breast lumps, it’s still always a good idea to make an appointment with a doctor as soon as growth is detected especially if there are changes in a tumor that was previously diagnosed as benign, including growth or a change in symptoms. Remember – Anything that looks abnormal should be evaluated by a doctor.