Cancer occurs when the cells divide uncontrollably and destroy the body tissue. When cancer originates in reproductive organs, it is termed as gynecological cancer. Gynecologic oncology is the field of study and practice that deals with the tumors of the female genital tract.
The term ‘Gynaecological Cancers’ comes with the medical condition in which cancer or tumor cells develop in the reproductive organs of a woman’s body; these include cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, vaginal cancer, and vulvar cancer.
There are several symptoms associated with gynecological cancers, each cancer type associated with specific symptoms and the best way to detect the right kind is getting the proper consultation done.
Gynecological cancers are one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in women worldwide. Lakhs of women are diagnosed with gynecological cancers and hence, it is important to be aware of the various types of gynecological cancers.
There are six types of gynecological cancers of which three are common and the other three are rare which are listed below.
- Uterine cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Vulvar cancer
- Vaginal cancer
- Gestational trophoblastic tumour
Most Common Gynecological Cancers:
The following types of gynecological cancers are quite common and affect a large number of women every year:
1. Uterine cancer:
Uterine cancer is cancer that begins in the uterus and is one of the most common types of gynecological cancers. Though it can happen to anyone, some factors which increase the risk of uterine cancer are obesity, diabetes, hypertension, use of estrogen without progesterone, etc.
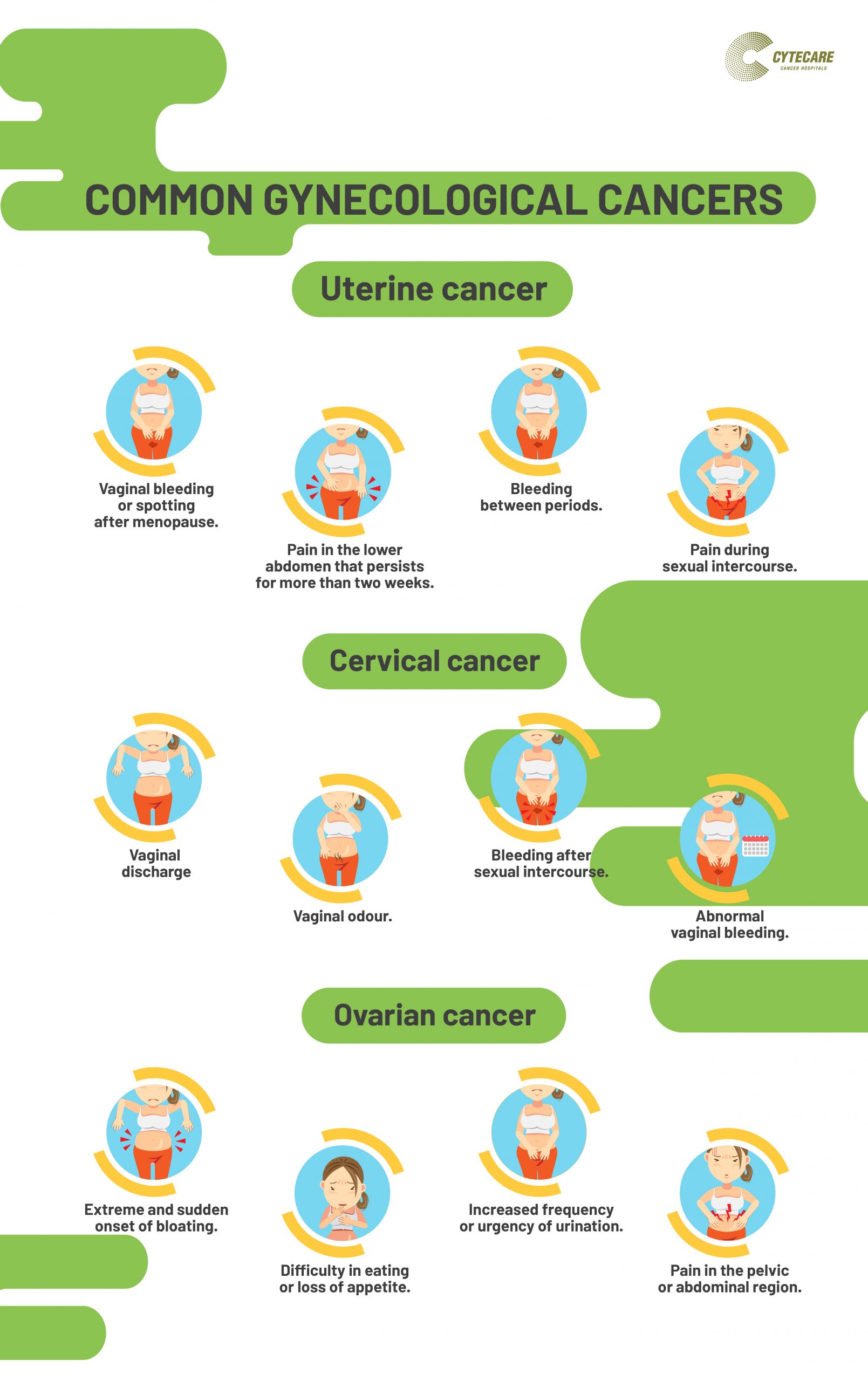
The common endometrial cancer symptoms are:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting after menopause. https://drwilliamhkoch.com/antabuse-online
- Pain in the lower abdomen that persists for more than two weeks
- Bleeding between periods.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
Uterine cancers can be further subdivided into endometrial cancers, uterine sarcomas, and endometrial stromal tumours. Of these, endometrial cancer is the most common type of uterine cancer and the other two are quite rare. Endometrial cancer is also one of the most curable ones.
Endometrial cancer is diagnosed quite early in most cases and hence is treated by a laparoscopic (minimally invasive) surgery. The entire treatment requires only 2-3 days of hospital stay in most cases. Though a few patients with endometrial cancer (about 10-15%) may require further treatment in the form of radiotherapy or a combination of radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
2. Cervical cancer:
Another very common type of gynecologic cancer is cervical cancer which is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in women worldwide. A large number of women in India are diagnosed with this cancer every year, and unfortunately, due to a lack of awareness and poor cancer screening facilities, a majority of women are diagnosed when cervical cancer has reached advanced stages. Also, a large number of cervical cancers are caused due to HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infection.
Some common cervical cancer symptoms include:
- Vaginal discharge.
- Vaginal odour.
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Regular cancer screenings and PAP tests for HPV detection are important for early detection. If diagnosed early, cervical cancer can be treated by radical surgery alone while those detected in advanced stages require a combination of chemo and radiation therapy.
Vaccinating young girls for preventing HPV infection before they are sexually active is a very effective way to prevent cervical cancers as well as many other forms of gynecological cancers.
3. Ovarian cancer:
Ovarian cancer is another common gynecological cancer. There are three types of it: epithelial ovarian cancer, germ cell cancer, and stromal cell cancer. Of these, epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common one accounting for about 85 per cent of all ovarian cancers.
Some common ovarian cancer symptoms are:
- Extreme and sudden onset of bloating.
- Difficulty in eating or loss of appetite.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Increased frequency or urgency of urination.
- Pain and discomfort in the pelvic or abdominal region.
The benign epithelial ovarian tumours can be cured by surgery and the malignant ones are treated by tumour cytoreductive surgery and chemotherapy. One important point to note about epithelial ovarian cancers is that they are quite aggressive and have a tendency to recur in an advanced stage. In such cases, treatment is done either surgically or through chemotherapy.
Germ cell tumour, another type of ovarian cancer, is usually seen in younger individuals and about 95% of these are curable by surgery alone while other cases may require additional chemotherapy. To treat germ cell tumours in young patients, fertility preservation therapy (sparing the other ovary and uterus) is usually preferred for treatment.
The third type of ovarian cancer i.e. stromal cell cancer is usually slow-growing in nature. A majority of such cases are treatable by surgery alone.
Rare gynecological cancers:
Some rarer forms of gynecological cancers are:
1. Vulvar cancer:
Vulvar cancer is a rare form of gynecological cancer and it affects the external female genitalia. It usually occurs in elderly women and is easily identifiable by the following symptoms:
- Red, pink, or white bumps having wart-like surface.
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating.
- Bleeding not associated with menstruation.
- Presence of white and rough patch in the region.
- A persistent open sore or ulcer.
Vulvar cancer is a highly curable type of gynecological cancer. In most cases, radical surgery is sufficient to treat vulvar cancer but some cases may require chemotherapy and radiation therapy as well.
2. Vaginal cancer:
Vaginal cancer is one of the rarest forms of gynecological cancer. It usually affects women over 50 years of age and in most cases, HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infection is responsible for cancer. The symptoms are:
- Presence of an obvious mass.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge.
- Pain during and after intercourse.
Similar to vulvar cancer, many cases of vaginal cancers are treatable with radical surgery while others may require radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
3. Gestational trophoblastic tumour:
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is a term used for a group of pregnancy-related tumours. These type of tumours are also quite rare and are further subdivided into five types (one benign and four malignant). These tumours usually start in the cells that would become placenta during pregnancy. The tumour starts in layers of cells known as trophoblast which surround the embryo and is mostly benign. These tumours are highly curable and are mostly treated with chemotherapy.
When it comes to diagnosis and gynecological cancer treatment, Cytecare provides you with unparalleled services. At Cytecare, we have a dedicated unit for women’s oncology and our diverse team includes gynecologists, oncologists, radiation oncologists, etc. who have years of experience in treating various gynecological cancers. Our medical expertise is complemented by state-of-the-art infrastructure providing you with the most advanced diagnostic facilities.