The National Cancer Institute states that ovarian cancer accounts for about 3% of all cancers in women. When it comes to deaths caused by cancer in the female reproductive system, the highest rank goes to ovarian cancer.
Ovarian cancer is sporadic but, the lack of early symptoms and effective screening tests makes ovarian cancer a fatal disease.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovaries are a part of the female reproductive system present on either side of the uterus that makes the eggs (ovulation process) and the female hormones. Every female is born with two functional ovaries. The eggs produced in the ovaries move to the uterus (where the fertilized egg settles in and develops into a fetus) through the fallopian tubes.
The ovaries are also responsible for making the female hormones, estrogen and progesterone. When a malignant tumor develops in any one or both of the ovaries, it is termed ovarian cancer.
The ovaries are mainly made up of 3 kinds of cells. Different cells can develop into different tumor:
Epithelial tumours:
This is the most common type. It begins from the cells that cover the outer surface of the ovary.
Germ cell tumours:
This kind of tumour starts from the cells that make the ova (egg).
Stromal tumours:
This kind of tumour begins from the tissue cells that produce the female hormones estrogen and progesterone and holds the ovary together.
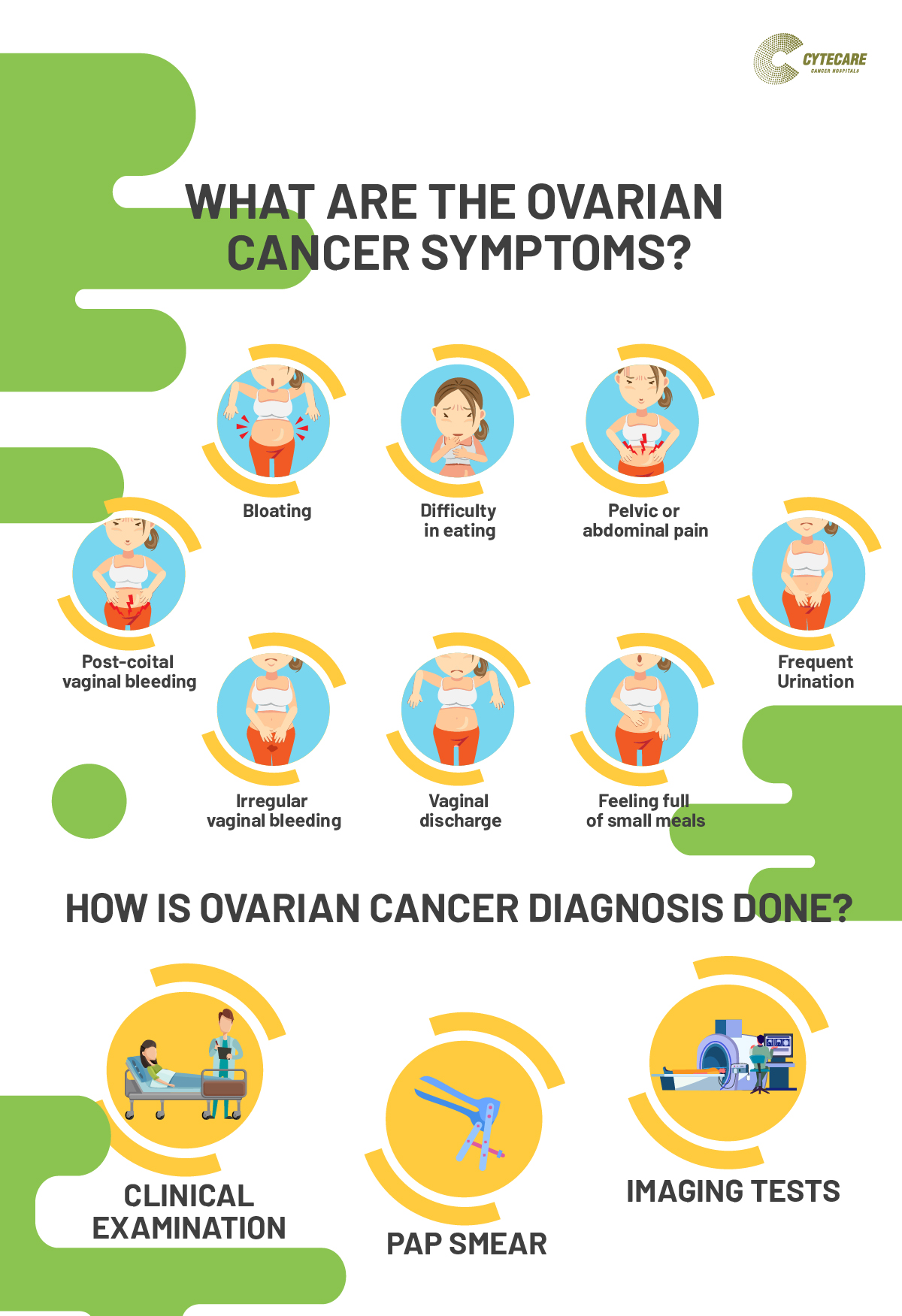
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
In the early stage it is very difficult to detect and may not have any symptoms (can be asymptomatic).
However here are a few of the possible symptoms:
- Bloating
- Difficulty in eating
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Frequent urination
- Feeling full of small meals
- Vaginal discharge
- Irregular vaginal bleeding
- Post-coital vaginal bleeding
These are the signs of benign (non-cancerous) or early cancer, if immediate medical attention is provided, it can even be cured.
Other symptoms of ovarian cancer are:
- Persistent pain or discomfort in the abdomen or pelvis
- Pain and swelling in the lower abdominal
- Change in the menstrual cycle
- Painful intercourse
- Frequent constipation
- Back pain that worsens with time
- Indigestion
- Fatigue and weight loss
- Acne
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer?
Diagnosis of ovarian cancer can be is carried out in many ways, a few of them are:
Clinical Examination
Clinical examination or physical examination or medical examination is a process by which a healthcare professional investigates the patient’s body for any signs of ovarian cancer. During the process, the doctor will ask the patient about his/her medical history to learn more about the possible risk factors, including family history.
Pap Smear
Pap smears are a diagnostic test that can detect any cancer associated with the female reproductive system. However, it does not screen for ovarian cancer. A Pap smear is an important test to detect and prevent cervical cancer. Getting a Pap smear done every 3 years is vital to detect cervical cancer.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are diagnostic procedure that involves taking pictures of the inside of the body to detect the presence of a pelvic mass and to see if the cancer cells have spread (metastasized) to other body parts.
A few of the commonly used imaging techniques are:
Ultrasound:
Ultrasound or ultrasonography is a technique that uses sound waves to create an image on a video screen. The probe is placed on the abdomen or in the vagina, and the transducer sends sound waves and picks up the echoes that bounce on the organs to create an image on the screen that is used to check if the abnormality present is a solid mass (tumor) or a fluid-filled cyst.
CT Scans or Computed Tomography Scans:
The CT scan is an x-ray that helps in detecting if cancer (ovarian) has spread to other organs by making detailed cross-sectional images of the body.
MRI Scans or Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans:
The MRI scan is not an x-ray test instead; a contrast material (gadolinium) is injected into a vein of the patient before the scan to see the details better. An MRI scan can help in finding if cancer has spread to other organs by making detailed cross-sectional images of the body.
Tumor markers blood tests:
Tumor markers are the biological chemicals produced or found in the tumour cells. The tumour markers blood test detects the presence of these chemicals in the blood of the patient.
Example:
- In the case of ovarian cancer, the test for cancer antigen 125 levels may be elevated, and the HE4 (human epididymis protein 4) levels may be elevated.
- In the case of germ cell tumours, the HCG, AFP & LDH levels of the patient are elevated.
- For stromal cell tumor, the level of inhibin B, AMH, estrogen and testosterone is elevated in the blood.
Treatments for Ovarian Cancer?
The treatment of ovarian cancer depends on the type and stage of cancer, and whether the patient wants to have children in the future or not.
The treatments are as follows:
Surgery
It is the primary form of treatment. Once the cancer is diagnosed, the affected and potentially affected organs are removed depending on if the patient wants to become pregnant in the future.
There are fertility preservation surgeries for the majority of the cases, which include sparing the uterus and unaffected other ovary and removing only the affected ovary with the tumor (along with the removal of lymph nodes and omentum).
The surgery can include:
- Laparoscopic surgery, if the tumors are smaller than eight cms in size or benign
- Peritoneal fluid washings for the analysis
- Surgically removing the abdominal and pelvic lymph nodes
- Surgically removing the affected ovary and a biopsy of the other suspicious abdominal and pelvic peritoneum or the other ovary
- Removal of the fatty tissue (or omentum) joined to the abdominal organs
In the case of the second, third, and fourth stages, the surgery may include the removal of the entire uterus, the ovaries and the fallopian tubes, the omentum, and the removal of tissues to which cancer has spread.
Chemotherapy
If cancer spreads to the nodes or omentum, further adjuvant chemotherapy is needed following the surgery. The chemo medication can be given to the patient intravenously or through the abdomen.
Surface epithelial ovarian tumors are the most common ovarian tumors. The less harmful epithelial (benign & borderline) tumours are cured by surgery.
A tumour cytoreductive surgery and chemotherapy treatment of the malignant epithelial ovarian cancers (harmful), and these cancers tend to recur again as they are aggressive and present in an advanced stage. Therefore, recurrent cancers are again treated by surgery if feasible or by chemotherapy.
The rare ovarian stromal tumours are slow-growing in nature and the majority of them are treated by surgery alone, only a few cases may need adjuvant chemotherapy.
Why Choose Cytecare Cancer Hospital?
Early detection of any form of cancer elevates the chances of successful treatment. So, keep an eye out for any changes you observe and get them checked at the earliest. You can trust Cytecare if you need more information.
At Cytecare we are “Fighting Cancer the Right Way” with highly specialized, modern diagnostic services, treatment and care for cancer patients. Guided by national as well as global protocols the multidisciplinary team of clinicians is highly qualified to help you fight cancer the right way. Give it a try!