Author:
Dr. Akshay Kudpaje, Senior Consultant & Director – Head & Neck Oncology
Overview of mouth(Oral) cancer
Mouth cancers develop within your mouth or oral cavity. Mouth cancer arises from the cells that line the mouth and oral cavity, the most common pathology being Squamous cell carcinoma. The oral cavity in one’s mouth is a part of the Head & Neck region which is involved in our daily activities like eating, drinking, speaking, etc., and hence, early diagnosis and treatment of mouth cancer is important to have better control over cancer and reduce the treatment side effects.
Is mouth cancer common in India?
Cancer is a non-communicable disease that has shown a dramatic rise in the developing world. Among the cancers, the mouth or oral cavity site is the most common cancer we encounter in India. Unlike the West, mouth cancer is a major public health problem in the sub-continent and ranks in the top 3 cancers in India. In India, 20 per 1,00,000 people are affected by mouth cancers, which accounts for about 30% of all types of cancer. It is the most common cancer among Indian males and 5th most frequent cancer in females.
Is mouth cancer a lifestyle-related disease?
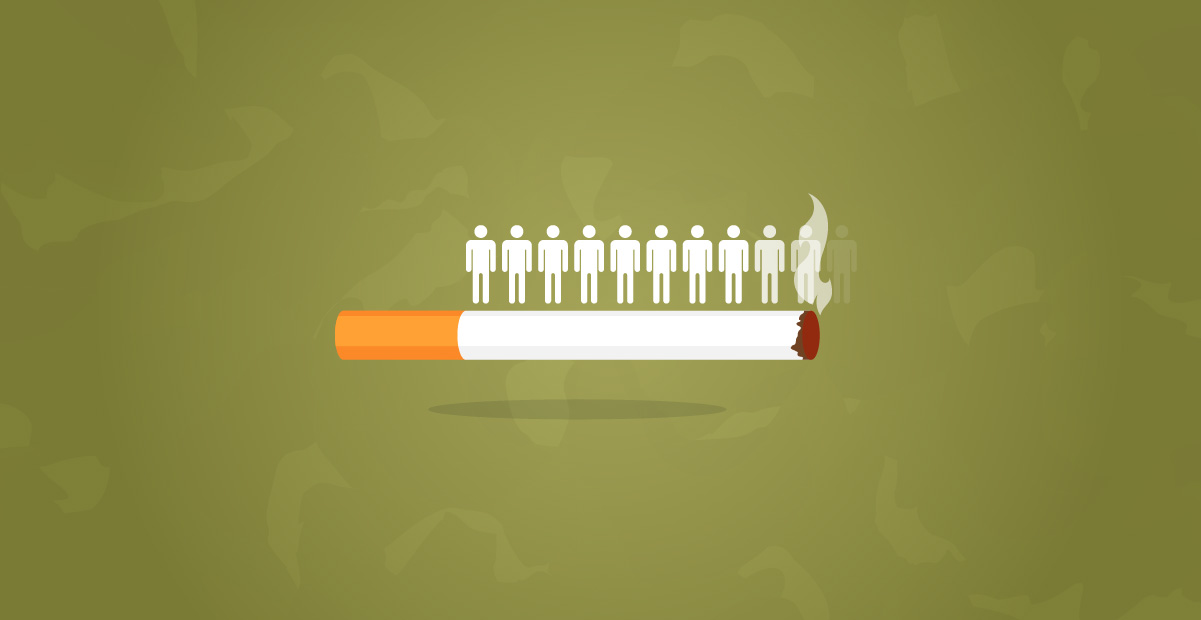
Mouth cancer is a preventable disease since it arises due to unhealthy lifestyle patterns, that is, from the consumption of tobacco and alcohol. Both tobacco and alcohol are carcinogenic, which means they contain chemicals that can damage the DNA in cells and lead to cancer. Smoking or drinking alcohol increases the risk of mouth cancer. Smoking and drinking combined multiplies the risk further.
The tobacco is consumed either in smoked or unsmoked form. The unsmoked form of tobacco consumption is common in India, which includes chewing betel nuts with or without added tobacco and chewing of various commercially available tobacco products like. Tobacco and alcohol consumption is the most common reason for mouth cancer in about 90% of the cases. Mouth cancer can occur even in patients without habits. The probable reasons for the development can be chronic irritation due to sharp tooth/dentures, HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) infection, poor dental hygiene, or nutrition deficiency.
How to detect cancers in an oral cavity?
In India, more than 60% of the diagnosed oral cancer patients present in an advanced stage (Stage III, IV). The cure rates of advanced cancers are around 20-40%, compared to early-stage cancers (Stage I, II) which is more than 80%.
The oral cavity is an easily accessible site for self-examination or assessment by medical professionals. The cost involved in diagnosing these lesions are minimal which involves simple examination with light and, if required, a biopsy that can be performed in the clinic.
The symptoms of mouth cancer include any mouth or lip sore or lump which doesn’t heal in 2 weeks, a white or red patch that cannot be wiped out, bleeding from the oral cavity, persistent pain in the mouth, difficulty in swallowing, loose tooth, and/or foul smell in the oral cavity.
Treatment options of mouth cancers
Surgery, Radiation and Chemotherapy are the three main treatment modalities available for mouth cancer. Among these, surgery is the first preferred modality of treatment. Early-stage (I, II) cancers are treated with surgery alone. In advanced stage (III, IV) cancers, surgery will be followed with adjuvant therapy in the form of radiation therapy, with or without chemotherapy based on high-risk features on the histopathology report.
There has been significant development in surgery in recent times where the tissue lost due to surgery is replaced during the same operation to achieve better functional outcomes in the form of speech, swallowing, and cosmesis.
Rehabilitation after oral cavity cancer treatment is the key to achieving the best outcomes. A group of allied specialists that include a Dental surgeon, Speech & swallowing therapist, Physiotherapist, Psychologist, Dietician, and Yoga therapist work as a team to assist the patients after treatment.